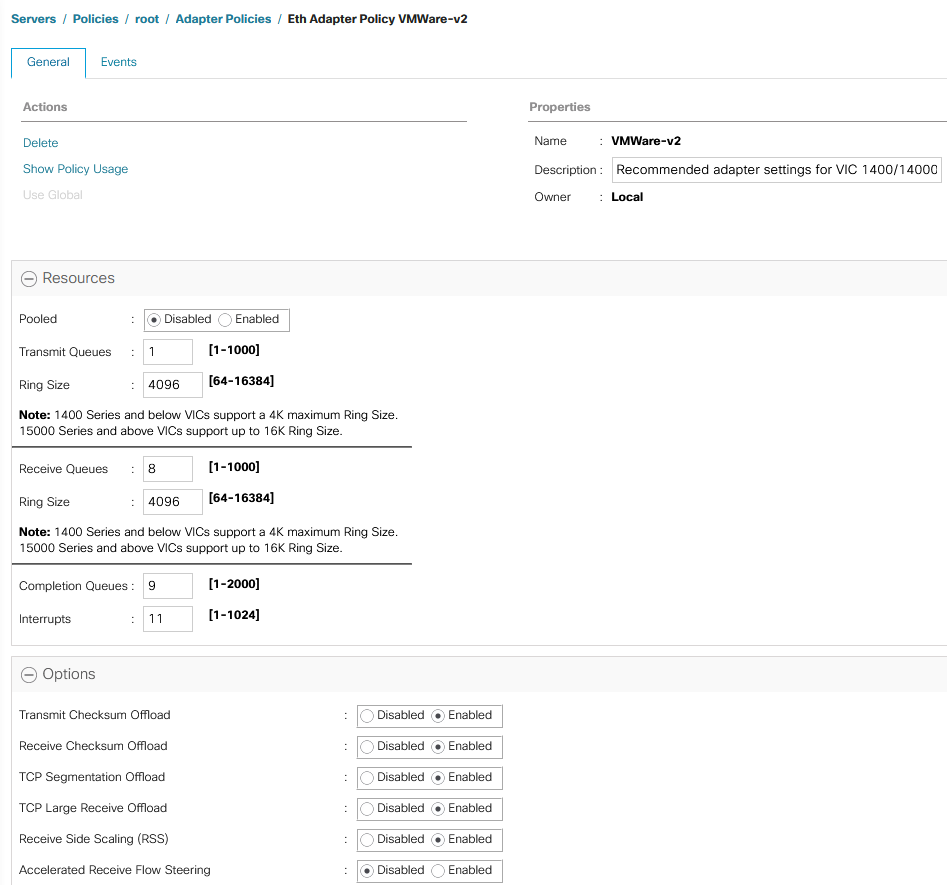
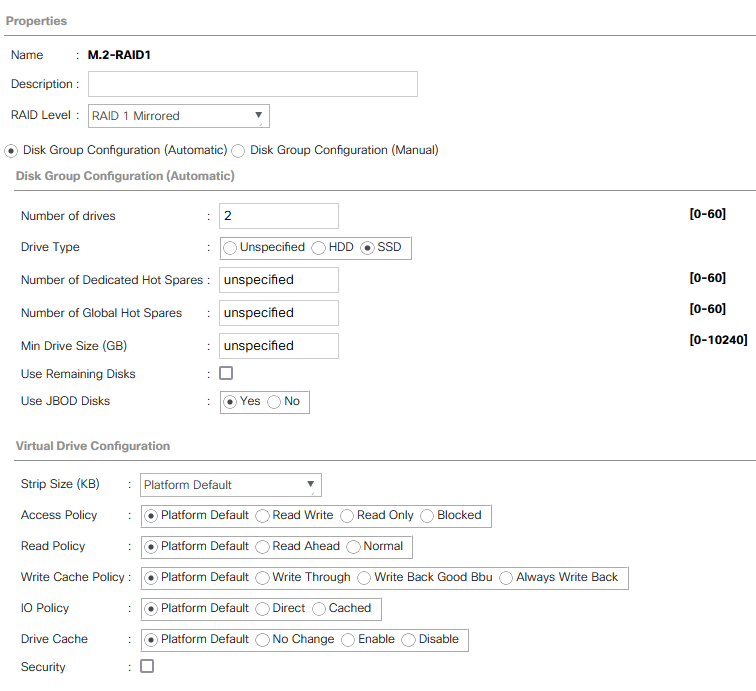
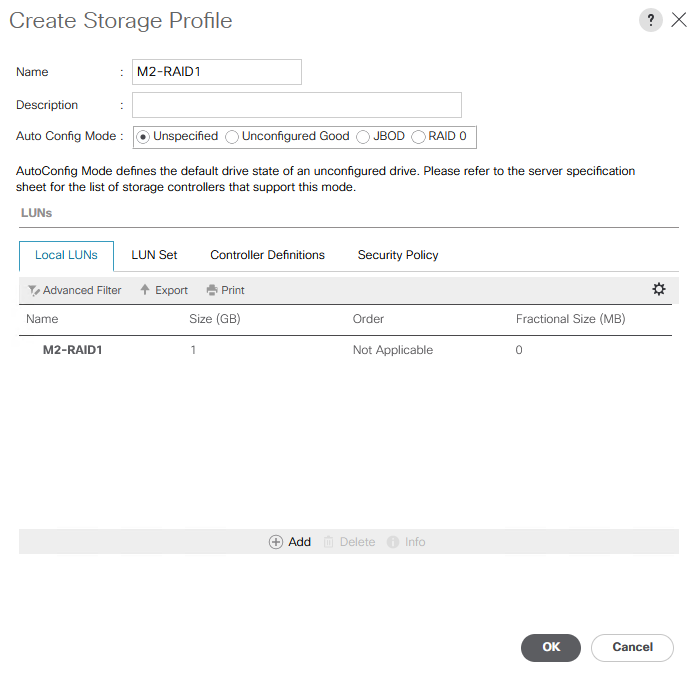
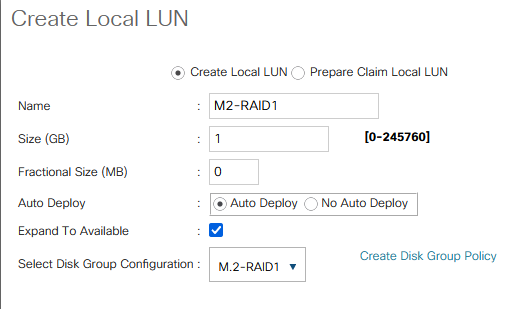
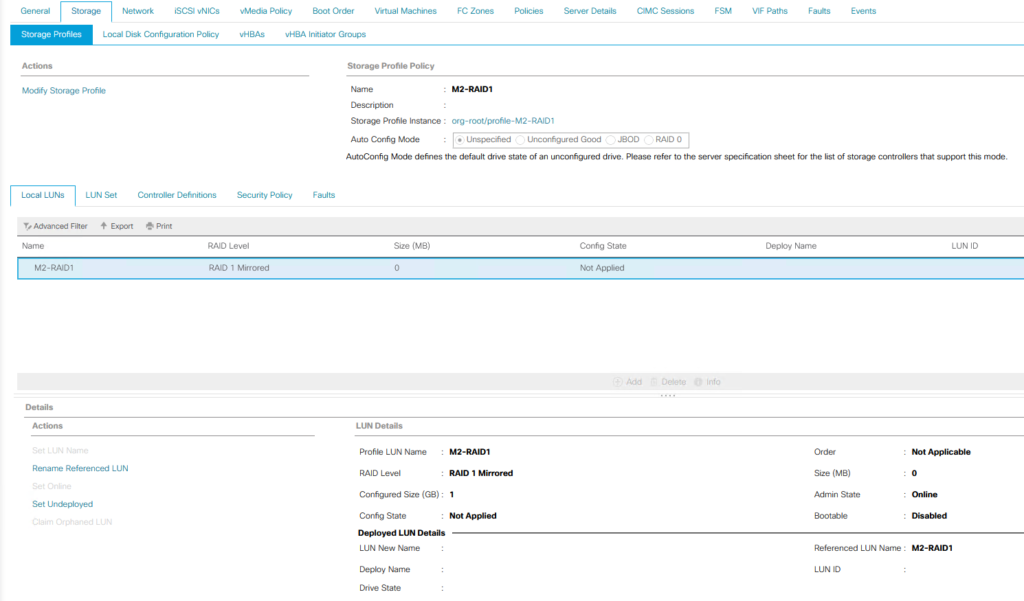
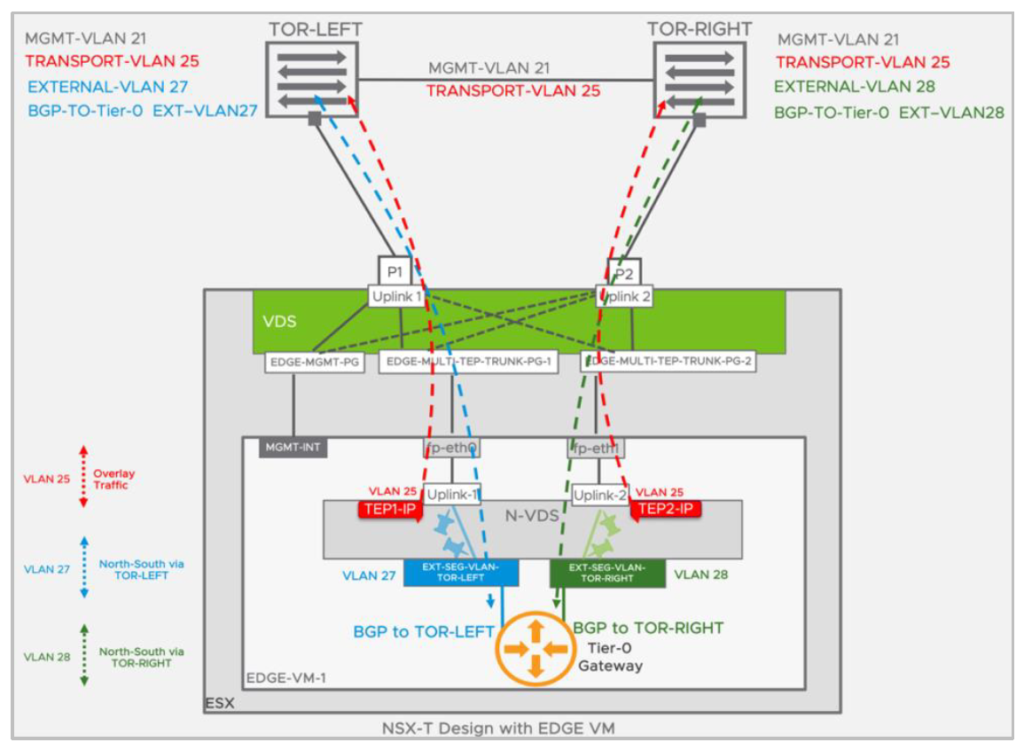
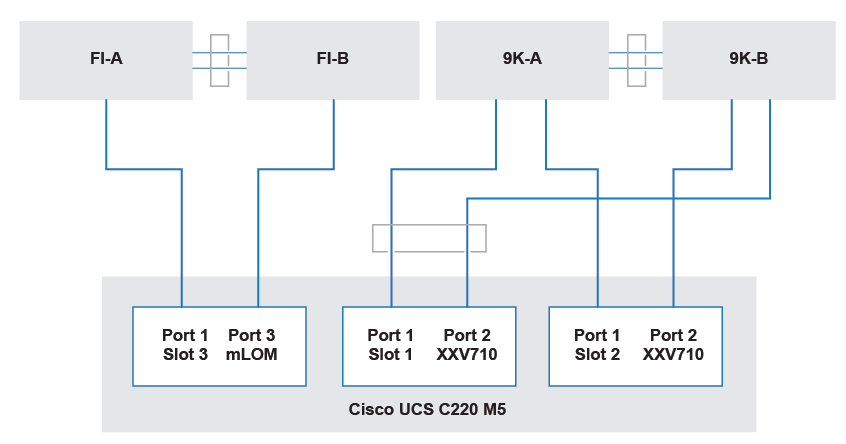
With the Cisco UCS 4.3(5a) release, Cisco addresses multiple critical security vulnerabilities impacting UCS Manager, Fabric Interconnects, and compute nodes. These updates are essential for maintaining secure infrastructure as they address several vulnerabilities within third-party software dependencies. Here’s a rundown of the significant security fixes provided in this release.
1. CSCwb81661: Vulnerabilities in OpenSSL
Cisco UCS Manager now includes critical fixes for three vulnerabilities related to OpenSSL, which, if exploited, could impact cryptographic functions, certificate parsing, and script handling. Here’s a closer look at each vulnerability:
- CVE-2021-4160: A bug in the squaring procedure of MIPS32 and MIPS64 processors could potentially allow attackers to exploit Diffie-Hellman (DH) cryptographic operations, which affects scenarios with shared DH private keys. Cisco has mitigated this vulnerability by upgrading to fixed OpenSSL versions, addressing this issue in OpenSSL 1.1.1m, 3.0.1, and later releases.
- CVE-2022-0778: The BN_mod_sqrt() function in OpenSSL could enter an infinite loop when parsing certain elliptic curve certificates, leading to a denial of service (DoS). This could be triggered in scenarios involving TLS and certificate handling. Cisco’s update mitigates this risk with fixes provided in OpenSSL 1.1.1n, 3.0.2, and later versions.
- CVE-2022-1292: A vulnerability in the
c_rehashscript could allow attackers to inject commands through improperly sanitized shell metacharacters. This script, now considered obsolete, is replaced by OpenSSL’srehashcommand-line tool, which Cisco has now included to remove this potential risk.
2. CSCwk62264: OpenSSH Security Regression (CVE-2024-6387)
Cisco UCS 6400 and 6500 Series Fabric Interconnects, when operated in UCS Manager mode, were vulnerable to a security regression in the OpenSSH server (sshd). This flaw, stemming from an older race condition vulnerability (CVE-2006-5051), could allow unauthenticated attackers to exploit the sshd signal handling.
Cisco’s Solution: Cisco has patched OpenSSH within the UCS software stack, reinforcing the security of SSH operations in Fabric Interconnects to eliminate this race condition vulnerability.
3. CSCwk62723: OpenSSH Vulnerability in Serial over LAN (SOL) on Blade Servers and Compute Nodes
The UCS B-Series Blade Servers and X-Series Compute Nodes were also affected by the same OpenSSH race condition issue. This vulnerability could impact serial-over-LAN connections, which are essential for remote console access.
Cisco’s Solution: The update fixes this vulnerability by integrating the latest OpenSSH patch, safeguarding remote management sessions on UCS blade servers and compute nodes.
4. CSCwk75392: libexpat Denial of Service Vulnerability (CVE-2023-52425)
This vulnerability in libexpat could lead to a denial of service (DoS) attack due to resource-intensive parsing of large tokens. Cisco UCS Manager, which relies on libexpat for XML parsing, could be affected in scenarios that involve extensive parsing requirements.
Cisco’s Solution: The upgraded libexpat version now included in UCS Manager resolves this DoS vulnerability, ensuring that XML parsing operations are resilient against such resource exhaustion attacks.