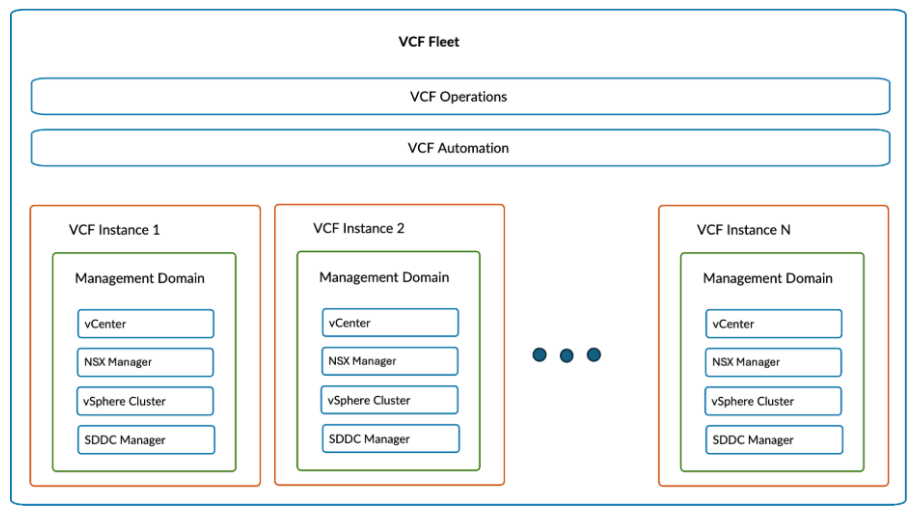
Ready to unleash true self-service private cloud automation? VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) 9.0 is packed with robust automation features, and the HOL-2610-02-VCF-L lab is your guided hands-on tour to master them.
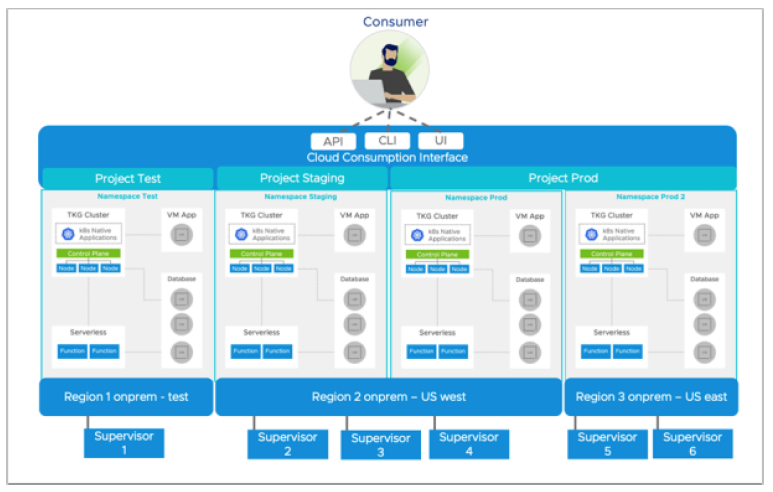
Whether you’re a cloud admin, service provider, or an automation enthusiast, this lab takes you from zero to hero, showing you exactly how VCF 9.0 streamlines infrastructure operations, enforces governance, and accelerates modern application deployment. Here’s an inside look at what you’ll experience.
🎓 Module 1: Getting Started with VCF Automation
⏱️ Length: 15 min | Level: Beginner
You’ll kick things off with the new Quick Start Wizard, a major usability boost in VCF 9.0. It offers both manual and automated workflows to configure your environment in minutes.
💡 Lab highlight: Experience an interactive simulation that mimics a real deployment—perfect if you want to see the process without spinning up actual infrastructure.
🗂️ Module 2: Dive Into the Provider Portal
⏱️ Length: 15 min | Level: Beginner
The Provider Portal is your mission control. In this module, you’ll:
✅ Explore the Infrastructure Overview—see organizations, regions, supervisors, and content libraries at a glance.
✅ Configure Access Control—add users, assign or create custom roles, and manage permissions.
✅ Connect Identity Providers—integrate OIDC, LDAP, or SAML for centralized authentication. Bring your enterprise-grade security posture directly into VCF Automation.
🏢 Module 3: Master Organization Management & Governance
⏱️ Length: 30 min | Level: Advanced
Here’s where things get powerful:
✨ Content Libraries: Learn to create tenant-specific libraries to manage VM images and deployment blueprints. Unlike provider libraries, these are isolated per organization, supporting granular control.
🔑 IaaS Policies: Enforce compliance automatically. Create policies to govern how resources are provisioned and what users can do post-deployment. For example, the lab guides you through setting an IaaS Resource Policy to block unauthorized VM deployments—then tests it live to see policy enforcement in action.
🧭 Governance Tools: Leverage centralized billing, resource sharing, and collaboration while keeping strict security boundaries between tenants.
☁️ Module 4: Deploying Modern Applications
⏱️ Length: 30 min | Level: Advanced
This final module shows how VCF 9.0 transforms modern app delivery:
🐳 Supervisor Clusters: Understand how vSphere Supervisor and Namespaces abstract infrastructure complexity, letting users consume IaaS resources through Kubernetes APIs.
⚙️ Blueprint Design: Hands-on time! You’ll deploy:
- A Virtual Machine using a pre-defined blueprint and YAML.
- A Kubernetes Cluster with just a few clicks.
🔍 Day 2 Operations: Explore post-deployment operations—view resources, manage them through intuitive interfaces, and understand the cloud-native approach to scaling and managing workloads.
✅ Why This Lab is a Must-Try
By the end of HOL-2610-02-VCF-L, you’ll have practical experience with:
- Building tenant organizations
- Managing user access and identities
- Enforcing organizational policies
- Deploying VMs and Kubernetes clusters on-demand